Plastic waste is one of the biggest environmental challenges India faces today. However, modern recycling technologies are transforming waste into valuable resources. One of the most promising innovations is the production of recycled polyester, commonly known as rPET.
The rPET manufacturing process converts discarded plastic bottles into high-quality fibers and fabrics used across fashion, home textiles, and industrial applications. This process not only reduces landfill waste but also conserves energy and lowers carbon emissions.
Understanding the rPET manufacturing process helps manufacturers, brands, and consumers appreciate how plastic waste can become sustainable textiles. In this technical guide, we break down each stage of the journey — from bottle collection to finished fabric by Rudra Ecovation
What Is rPET?
rPET stands for recycled polyethylene terephthalate. It is a form of polyester made by recycling PET plastic bottles instead of using virgin petroleum-based raw materials.
Compared to virgin polyester, rPET:
-
Uses less energy
-
Reduces plastic waste
-
Produces fewer emissions
-
Supports circular economy practices
These benefits make the rPET manufacturing process central to sustainable textile production in India.
Step-by-Step rPET Manufacturing Process
Step 1: Collection of Used PET Bottles



The rPET manufacturing process begins with systematic collection.
PET bottles are gathered from:
-
Households
-
Offices
-
Commercial spaces
-
Waste pickers and aggregators
-
Municipal waste streams
Collected bottles are sorted and compressed into bales for easy transportation to recycling plants.
Efficient collection ensures a steady supply of recyclable material.
Step 2: Sorting and Segregation
Once bottles arrive at the facility, they undergo sorting.
This step removes:
-
Non-PET plastics
-
Metals
-
Paper labels
-
Caps and closures
-
Contaminants
Advanced systems use:
-
Optical sensors
-
Manual inspection
-
AI-based sorting
Accurate segregation is critical because contamination reduces the quality of recycled output.
Sorting is a crucial stage of the rPET manufacturing process that directly impacts final fabric performance.
Step 3: Washing and Cleaning



After sorting, bottles are thoroughly cleaned.
The washing stage includes:
-
Pre-rinse
-
Hot water wash
-
Chemical treatment
-
Label and glue removal
-
Drying
This removes:
-
Dirt
-
Oils
-
Food residues
-
Adhesives
Clean input material ensures high-quality recycled polyester.
Without proper cleaning, the rPET manufacturing process cannot produce textile-grade fibers.
Step 4: Shredding Into Flakes
Clean bottles are then shredded into small pieces known as PET flakes.
These flakes are:
-
Lightweight
-
Easy to process
-
Uniform in size
The flakes serve as the base raw material for further processing.
This mechanical transformation marks the first conversion from bottle form into reusable plastic feedstock.
Step 5: Melting and Pelletizing
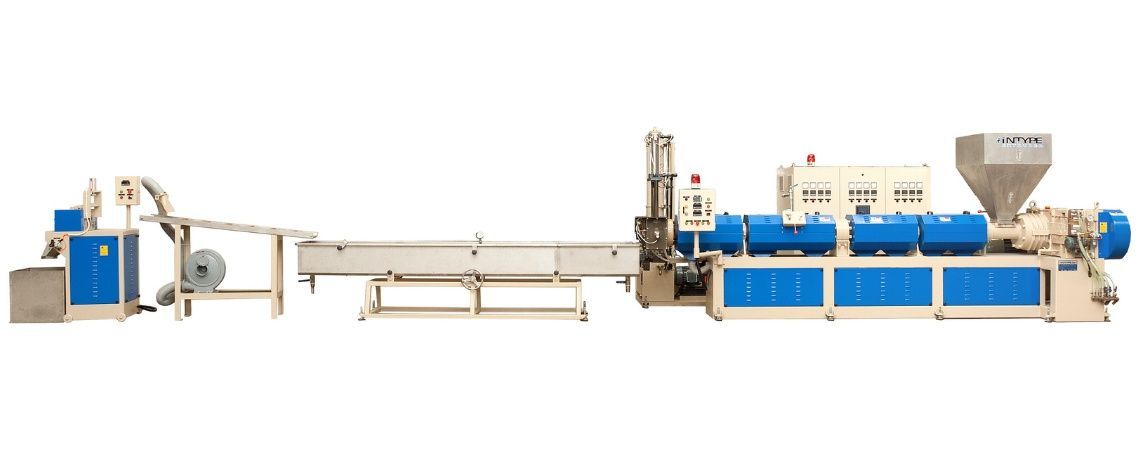


Next, flakes are melted at high temperatures.
The molten plastic is:
-
Filtered to remove impurities
-
Extruded into strands
-
Cut into small pellets or chips
These pellets become the core input for fiber production.
This stage defines the industrial heart of the rPET manufacturing process, converting waste plastic into standardized raw material.
Step 6: Fiber and Yarn Production
Pellets are reheated and pushed through spinnerets to form thin polyester filaments.
These filaments are:
-
Stretched for strength
-
Cooled
-
Texturized
-
Spun into yarn
The resulting recycled polyester yarn has properties similar to virgin polyester.
At this point, the rPET manufacturing process transitions from recycling into textile manufacturing.
Step 7: Fabric Manufacturing



The yarn is then converted into fabric through:
-
Weaving
-
Knitting
-
Dyeing
-
Finishing
The final product becomes:
-
Apparel fabrics
-
Sportswear textiles
-
Upholstery materials
-
Industrial fabrics
These fabrics perform just like traditional polyester but with a much smaller environmental footprint.
Environmental Benefits of the rPET Manufacturing Process
The rPET manufacturing process delivers several sustainability advantages:
Reduces Plastic Waste
Diverts bottles from landfills and oceans.
Saves Energy
Consumes less energy than virgin polyester production.
Lowers Carbon Emissions
Reduces greenhouse gases significantly.
Conserves Resources
Minimizes petroleum usage.
Supports Circular Economy
Turns waste into valuable products.
Why rPET Production Matters for India
India has:
-
Large plastic waste volumes
-
Strong textile manufacturing capabilities
-
Growing sustainability awareness
Combining recycling with textiles creates huge opportunities.
Expanding the rPET manufacturing process helps India:
-
Reduce environmental pollution
-
Strengthen recycling infrastructure
-
Create green jobs
-
Build sustainable supply chains
This makes recycled polyester a strategic solution for both waste management and industrial growth.
Challenges in rPET Manufacturing
Despite benefits, some challenges exist:
-
Collection inefficiencies
-
Contamination risks
-
High initial investment
-
Quality control requirements
However, advanced technologies are addressing these issues rapidly.
As processes improve, the rPET manufacturing process becomes more efficient and cost-effective.
Conclusion
The journey from bottle to fabric is a remarkable example of circular innovation. The rPET manufacturing process shows how waste can be transformed into high-performance, sustainable textiles through systematic recycling and advanced technology.
By converting discarded plastic into yarn and fabric, industries reduce pollution while creating economic value.
As sustainability becomes central to manufacturing, rPET production will continue to play a crucial role in shaping India’s greener future.
Every recycled bottle brings us one step closer to a cleaner and more circular world.